Bazel 7 is here - and Bazel Invocation Analyzer is ready for it!¶
On December 11th, 2023, Bazel 7.0 LTS was released, which includes multiple changes to improve build performance. More details below!
Bazel Invocation Analyzer (BIA) is an open-source tool by EngFlow that analyses the JSON trace profiles generated by Bazel and provides suggestions on how to improve the build performance. You can download the source and run the CLI or use the web UI available at https://analyzer.engflow.com.
BIA has been updated to support the internal changes introduced with the launch of Bazel 7.0 LTS, so you can continue to speed up your builds with the help of BIA. It also features new types of suggestions to help you fine-tune your builds irrespective of whether you are using Bazel 7 already or not.
Changes included in Bazel 7.0¶
The release of Bazel 7.0 LTS includes multiple significant changes, including:
Bzlmod enabled by default¶
Bzlmod is Bazel's new system for managing external dependencies. While
specifying third party dependencies in your WORKSPACE is still possible, that
option is scheduled for removal with Bazel 9. If you haven't yet, now is a good
time to look at the migration guide.
You may also use BIA's migration to Bzlmod for a hands-on example.
Build without the Bytes enabled by default¶
Build without the Bytes can reduce the amount of data transferred between Bazel and a remote caching or execution system and can speed up builds by up to 40%. It also enables Bazel to gracefully handle remote cache evictions.
The new default value is toplevel. Use minimal for additional savings if you
if you are only interested in build and test results, but not artifacts, for
example for CI.
You can change the behavior using the flag
--remote_download_outputs.
Check the related Bazel blog post for details.
Skymeld enabled by default¶
Skymeld interleaves Bazel's analysis and execution phases, which can reduce the end-to-end wall time of multi-target builds by up to 15%.
You can disable this feature (e.g. for benchmarking) using the flag
--experimental_merged_skyframe_analysis_execution=false
.
Built-in Android rules changes¶
Platform-based toolchain resolution is now enabled for Android and C++. If you
have an Android project, replace the use of --fat_apk_cpu with --android_platforms to specify which
device you want your APKs to build for.
Check the related Bazel blog post for details.
Bazel Invocation Analyzer changes¶
Example Bzlmod migration¶
Inspired by the Bazel 7 release, we migrated BIA from using a WORKSPACE file
to Bzlmod. The related tracking issue may be used as a simple
migration example, which includes
- [#144]: depending on other modules available in the Bazel Central Registry,
- [#149, #160, #161] using
rules_jvm_externalto pull artifacts from Maven: - [#153]: using
buildifier_prebuiltto lintBUILDfiles, and - [#159]: introducing a Bazel lockfile.
Analysis changes¶
Enabling Skymeld significantly changes how Bazel processes targets, which is also reflected in changes to the JSON trace profile Bazel writes. The BIA code has been updated and now supports analyzing profiles that were generated with Skymeld enabled.
Example analysis
Suggestions as presented on https://analyzer.engflow.com
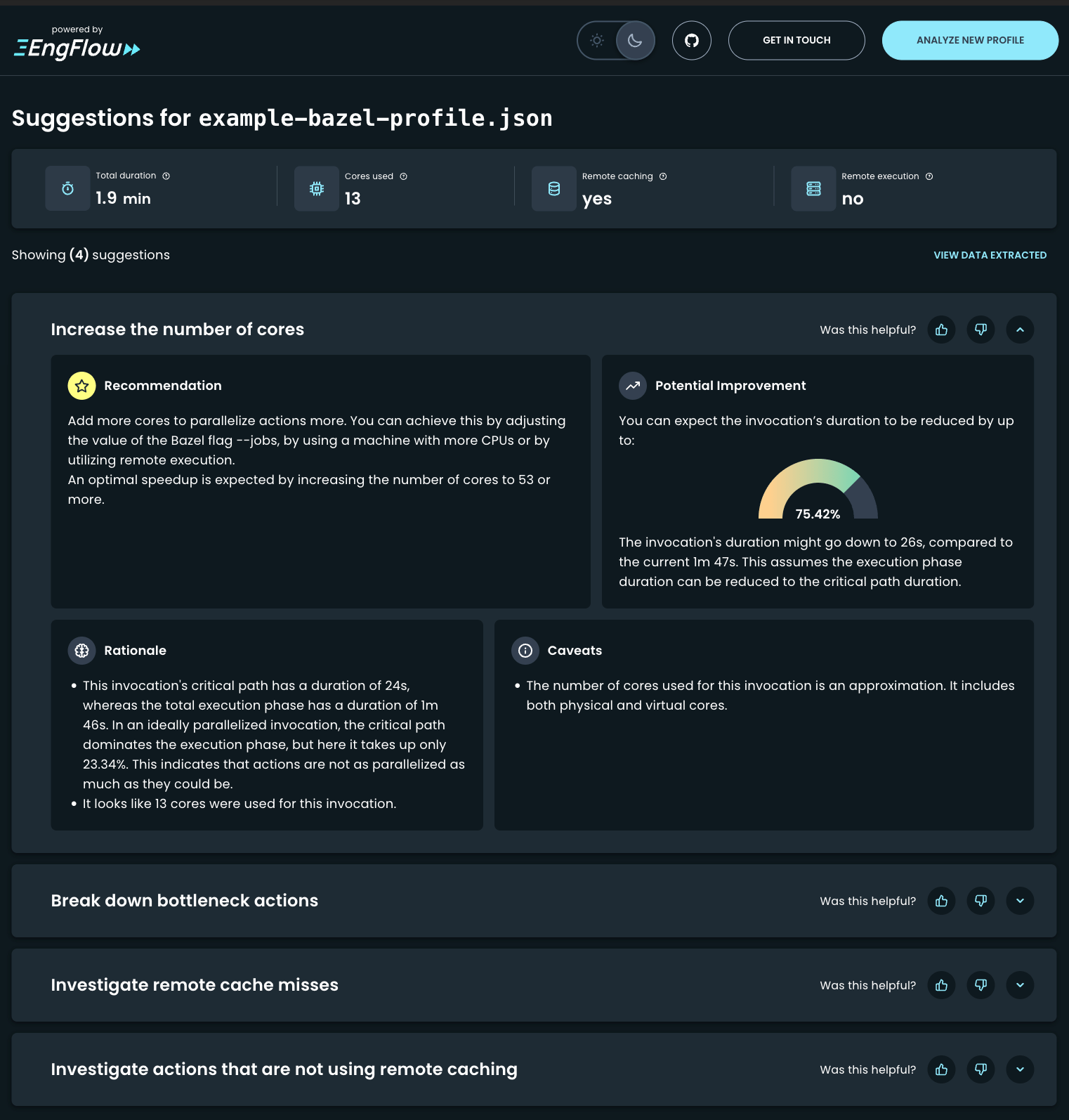
Additionally, here are some recent additions to the BIA analysis:
Suggest enabling Skymeld¶
BIA now detects whether Skymeld was enabled. If not, it suggests enabling Skymeld for future invocations, as this has been shown to reduce the build time by up to 15%.
Suggest using remote caching¶
BIA now suggests using remote caching, if it was not used. This includes
using --disk_cache, which uses your
file system, rather than a remote serivce. It also highlights that --remote_cache and --disk_cache can be combined and is
recommended in most cases.
Remote cache and execution location statistics¶
BIA now collects how many actions checked the remote cache, how many were hits hits or misses, and how much time was spent checking for cache hits, downloading outputs (for cache hits) and uploading outputs (for cache misses). For actions without a cache hit (misses or actions that do not check the remote cache), it also includes whether they were executed locally or remotely.
Highlight most expensive cache misses¶
BIA now lists the cache misses whose execution took the longest. Converting these to cache hits has the highest potential to significantly speed up builds.
Highlight most expensive cache skips¶
When using remote caching, the analyzer now lists the actions that did no check the remote cache and took the longest to execute. Leveraging the remote cache for these has the highest potential to significantly speed up builds.
Migrate local actions when remote execution is used¶
If remote execution was used, the analyzer list the longest-running local actions and suggests migrating them to remote execution, too. This can speed up invocations and improve their hermeticity.
Contribute¶
Bazel Invocation Analyzer is an open-source project and we welcome contributions. To get started, watch the the BazelCon 2022 talk on BIA or check out the documentation.
